Vacuum Heat Treating
NEO – The Future of Vacuum Oil Quenching
Despite decades of relentless innovation, the constraints of high-pressure gas quenching have become increasingly evident. Even with the utilization of specialized inert gas blends and heightened gas pressures, the gas cooling efficacy compared to liquid quenchant cooling particularly for heavier cross sections has its limitations.
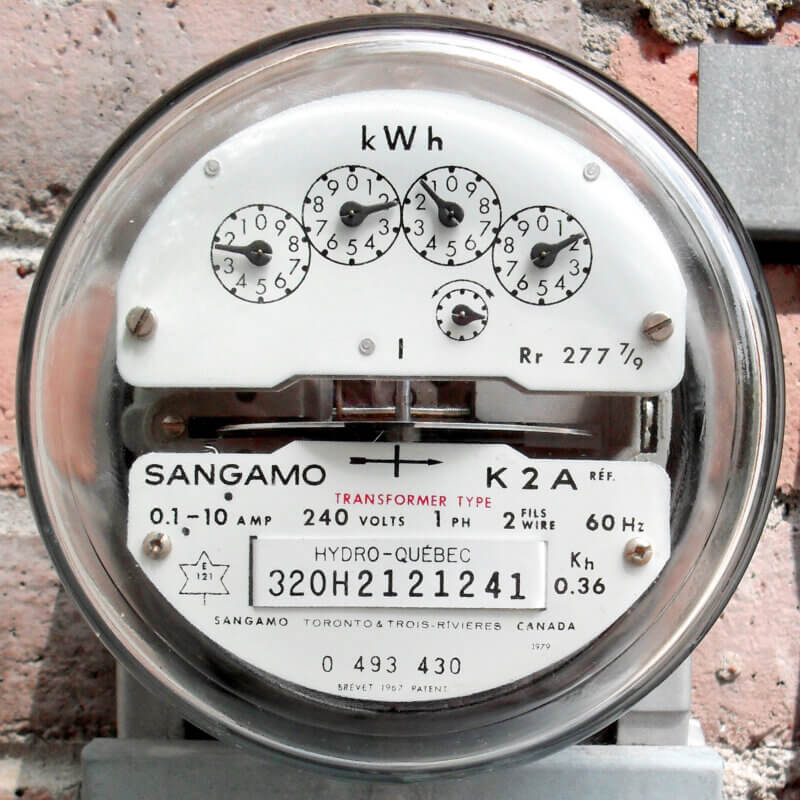
Conserve Electric Power and Save Dollars in Vacuum Processing
Generally, electric power consumption is insidious because it is not seen and is not considered enough by operating personnel. The following is a summary of power consumed in a typical heat treat plant.
Improving the Safety and Quality of Medical Devices Through Heat-Treating Process Accreditation
Technological change in many industries is often driven by advances in basic science, a move to digital transformation or simply the disruption of the status quo. In manufacturing, the focus on the ability to maintain a process with precision and repeatability based on supply-chain management is also crucial and has led to important advances in industries that make safety and quality imperative.
Preventing Eutectic Reactions and Diffusion Bonding in Vacuum Processing
The purpose of this paper is to explain reactions that can occur during a vacuum processing cycle and different methods of preventing these reactions.
Titanium: A Fascinating History and Future
For all the advances, titanium and its many alloys, has not reached its apex in popularity in the world. Is there any other element that calls to mind the notion of strength quite like titanium?
Vacuum Gas Cooling – Is Pressure or Velocity Most Important? (Part 1)
There is an age-old adage that exists in the heat treating world. That supposition states that “the smaller the vacuum furnace, the faster it will quench.” Our study compared the cooling rates of two distinctly sized High Pressure Gas Quenching (HPGQ) vacuum furnaces- a large 10-bar vacuum furnace equipped with a 600 HP blower motor versus a smaller 10-bar vacuum furnace equipped with a 300 HP motor.
The Use of Graphite for Vacuum Furnace Fixturing
The vacuum furnace industry has searched for many years for the ideal material to be used in fixtures and grids for processing workloads at elevated temperatures. The support structures should be lightweight to achieve desired metallurgical results during the cooling phase of the process cycle.
Risky Business – The Vacuum Heat Treating of 3D Printed Components
As additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, continues to evolve, many challenges still plague this exciting new technology.
The Returning Need For the All-Metal Vacuum Furnace Hot Zone and Specific Application Advantages
In this article, we will highlight some of the essential design requirements needed to provide the proper all-metal furnace for these critical applications.
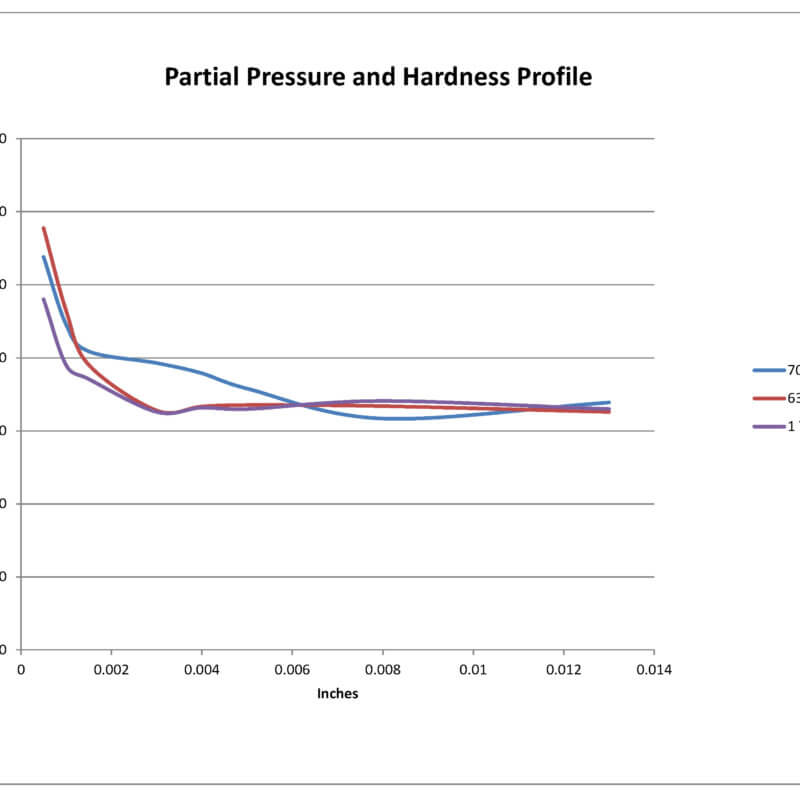
Gas Nitriding of Titanium
This preliminary study revealed that the partial pressure of nitrogen when gas nitriding Ti-6Al-4V in a vacuum furnace can have a significant effect on the nitrided case characteristics.